What is the meaning of lumbar stabilization and why is it important?
It is important to have a stable lumbar spine (low back) in order to prevent low backpain, dysfunction and disease. The lumbar vertebrae need to stay in normal alignment.By this we mean not too much forward flexion, backward extension, side bending orrotation. This is sometimes referred to as a “neutral spine” position.
The position of the pelvis can influence the alignment of the lumbar spine and contributegreatly to itʼs stability. The pelvis and lumbar spine work together in conjuction. Whenthe pelvis is unstable, the lumbar spine is unstable, when the pelvis is stable so is thelumbar spine.
 What causes an unstable pelvis and lumbar spine? Trauma, pregnancy and delivery, orsimple muscle imbalance. This unstable, misaligned pelvis and lumbar spine can notonly cause low back pain, but causes a “non-physiological axis of motion” through thelumbar spine which contributes to structural damage and degeneration. What is a “nonphysiologicalaxis of motion”? Think of this disrupted axis as a bent axle of a car. Whenthe axle is bent it causes the tires (or discs) to wear out much faster than normal. Notonly do the discs wear out much faster, but all of the structures in your lumbar spine willwear out faster, causing degenerative diseases like degenerative joint and disc disease,osteo arthritis contributing to stenosis, sciatica, scoliosis, etc.
What causes an unstable pelvis and lumbar spine? Trauma, pregnancy and delivery, orsimple muscle imbalance. This unstable, misaligned pelvis and lumbar spine can notonly cause low back pain, but causes a “non-physiological axis of motion” through thelumbar spine which contributes to structural damage and degeneration. What is a “nonphysiologicalaxis of motion”? Think of this disrupted axis as a bent axle of a car. Whenthe axle is bent it causes the tires (or discs) to wear out much faster than normal. Notonly do the discs wear out much faster, but all of the structures in your lumbar spine willwear out faster, causing degenerative diseases like degenerative joint and disc disease,osteo arthritis contributing to stenosis, sciatica, scoliosis, etc.

The Iliopsoas muscle
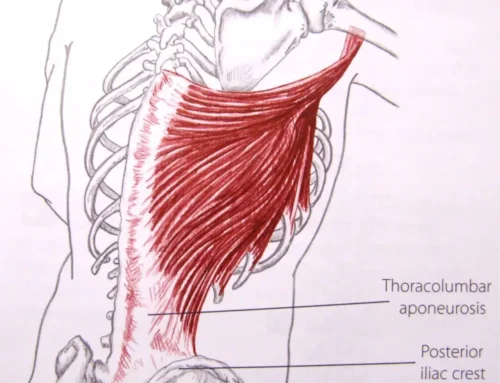
The muscles that tend to get too tight, short and spasmed that contribute to an unstablepelvis and lumbar spine are the right iliopsoas and left quadratus lumborum muscles.The muscles that tend to become too weak and let the pelvis and lumbar spine becomemore unstable are the gluteus muscles, the abdominal muscles and the hip abductormuscles.
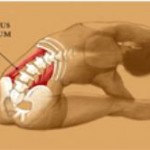 One needs to stretch the muscles that pull the pelvis and lumbar spine out of alignment(iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum) and strengthen the muscles that hold them inalignment (gluteus, abdominal and hip abductors). There are other muscles thatbecome spasmed as a result of an unstable lumbar spine and pelvis, however they areusually compensating for the above.
One needs to stretch the muscles that pull the pelvis and lumbar spine out of alignment(iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum) and strengthen the muscles that hold them inalignment (gluteus, abdominal and hip abductors). There are other muscles thatbecome spasmed as a result of an unstable lumbar spine and pelvis, however they areusually compensating for the above.
Body mechanics that tend to create the above mentioned muscle imbalances are prolonged sitting, repeated forward bending, sit-ups, working the latissimus dorsimuscles (including swimming) and backward bending against resistance. Sitting on awallet can also contribute to an unstable pelvis and lumbar spine
The exercises and stretches in the videos, “The Missing Link to Neck and Back PainRelief” demonstrate lumbar stabilization so that you can create a healthy spine. This is the first and laststep to creating a pain-free life!




I read a lot of interesting articles here. Probably you
spend a lot of time writing, i know how to save you a lot of time,
there is an online tool that creates readable, google friendly articles in minutes, just type in google – laranitas free content source
good morning! we have a lovely 20 month old girl who, for the past few days has had difficulty walking. she takes a few awkward steps with exaggerated tourso and arm movements, then squats and stretches her low back. she is falling more often and when she stands her pelvis slips anteriorly and posteriorly like it is giving out. her right leg gives out from time to time. she has had the exaggerated gait a few times in the past, but has always resolved within a day. she is tender on her low back and holds her hans back there when she walks and has to stand supported in some way. she does not run and is very trepidacious stepping down hill. she cannot find a comfortable laying position so getting to and remaining asleep is hard. when i picked her up on the first day of symptoms i heard and felt loud hard cracks from her lumbar thoracic junction. there is no redness, swelling, fever and does not feel hot. she did have one night of exessive urination and defication, but she also had some watermellon that day. i cannot find anything on toddler low back issues affecting gait and was wondering if you had any ideas or suggestions that may shed some light. we have been giving her oral nsaid elixir and her symptoms improve slightly for a few hours. any help would be greatly appreciated.
many thanks
ted